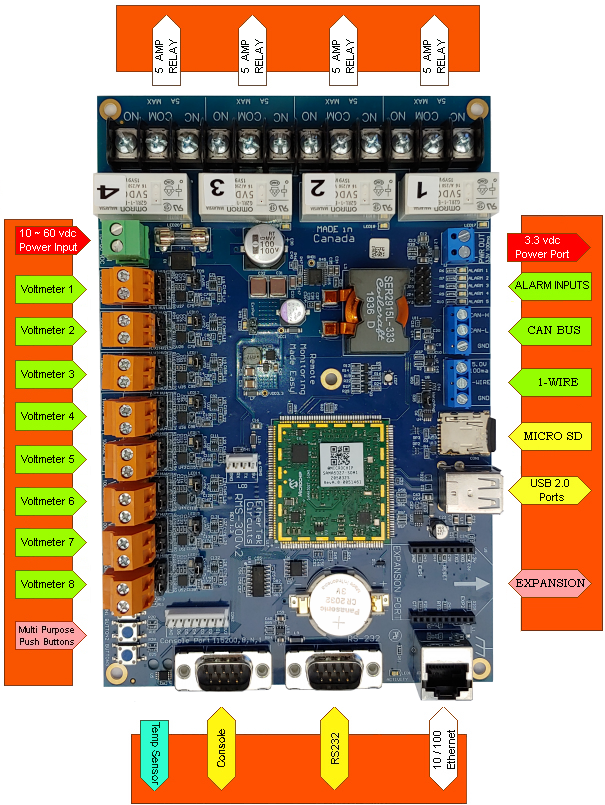
|
Installation
Basic Installation
Example 1
Measuring
your Battery Bank
To measure
your main battery power supply, run a wire from the positive side of the
battery bank to one of the ADC 0-30v positive inputs. Run a second wire
from the negative side of the battery to the corresponding ADC 0-30v negative
input as shown in Figure 2. Connect RMSv1 to the internet with
a common Ethernet cable and monitor the voltage level of your battery bank
with user friendly remote monitoring software. (As an alternative, a web browser
may be used to view RMSv1 output.)
Note:
The first two ADC inputs are special, as they can be configured for 30
volt or 60 volt operation. To configure ADC input number 1 for 60 volt
operation, simply remove the jumper from JP6. To configure ADC input number
2 for 60 volt operation, simply remove the jumper from JP7. When the jumpers
are installed, normal 0-30 volt operation is selected.

Figure 2
Basic Installation
Example 2
Signal
Strength on YDI Link CX Radio
Wireless
Inc � (now YDI �) radios have an external RSSI port. Checking signal strength by
climbing a tower with a voltmeter is difficult, expensive
and time consuming. RMSv1 makes this process much easier. Simply have
a cable made with a BNC connector at one end, attach the BNC connector
to the radio and run the cable into your equipment room. Strip the cable
so that the center core and outer shielding are separated. Twist the shielding
mesh together to form a single wire. Attach the solid center core to the
positive input on one of the RMSv1 Adc 5 volt inputs and attach the
twisted ground shielding to the negative input on the corresponding RMSv1
Adc 5 volt input (see Figure 3). Connect RMSv1 unit to the Internet
with a common Ethernet cable and monitor the signal strength of your radios
quickly and safely with the included user friendly remote monitoring software. (As
an alternative, a web browser may be used to view RMSv1 output.)

Figure 3
Basic
Installation Example 3
Turning
Devices ON/OFF
To make any device
remotely reset able, simply cut one of the wires in the power cord of
a device. Attach one side of the cut wire to the COM terminal on one of
the Power Relays. Attach the other side of the cut wire to the NC (normally
closed) terminal on the corresponding Power Relay. Reset your device at
any time using RMSv1 software. Note: in the Normally Closed
configuration, power still flows to your device even when the RMSv1 device
is turned off. Virtually any 1 to 240 volt AC or DC device can be
turned ON/OFF remotely this way. The two small Power Relays can pass up
to 5 amps each, the larger Power Relay up to 15 amps!. For devices
that should be by default turned off, use the COM and NO (normally open)
configuration. Figure 4 illustrates just one of the many ways you can set
up devices for remote reset.

Figure 4
Basic
Installation Example 4
Using the i/o pins to monitor door contacts
To give your equipment room some security you can
use widely available common door contacts. These contacts allow current to flow
through them when they are in close proximity with each other. RMSv1 can
sense when the contacts are together or apart. The diagram below (figure
5) shows how to use I/o pin 1 to monitor door contacts.
Note1: the LED1 light is on when the contacts are together and off when they are apart.
Note2: each I/o pin has a corresponding LED.
Note3: The pins marked GND and +5v are reserved for future expansion and should not be used.
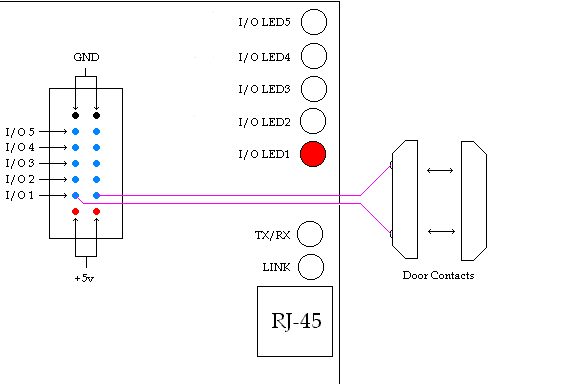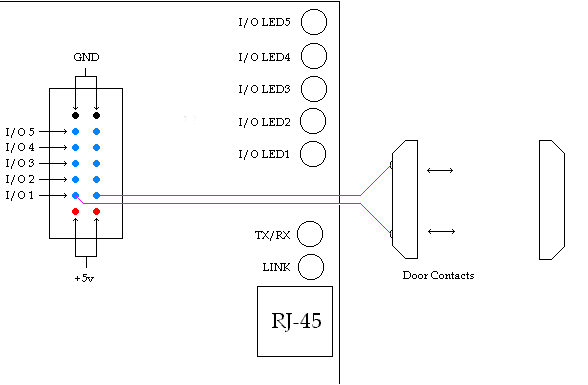
Figure 5
|